第 2 章 线性表
2.3.1. 单链表
链表倒序:头插法
// 带头节点的链表逆序Node* reverse(Node* head) { Node* p = head->next; head->next = NULL; for (Node* q = p; p != NULL; p = p->next) { q->next = head->next; head->next = q; } return head;}找到两个链表第一个公共节点
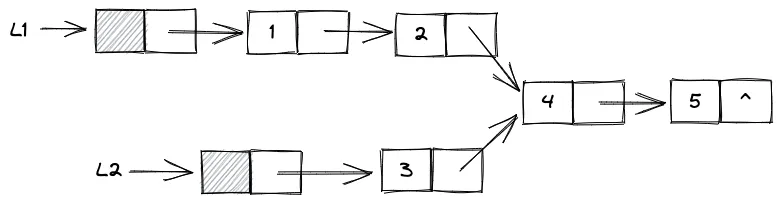
- 遍历两个链表,得到两个链表的长度
- 将两个链表尾端对齐,长的那个链表先走 步
- 共同步进,直到两个指针指向同一个节点
int listLength(Node* L) { int count = 0; for (Node* p = L->next; p != NULL; p = p->next) count++; return count;}
Node* commonNode(Node* L1, Node* L2) { int len1 = listLength(L1); int len2 = listLength(L2); Node* p = L1->next, * q = L2->next; int i; for (i = len1; i > len2; i--) p = p->next; for (i = len2; i > len1; i--) q = q->next; for (; p != NULL && q != NULL && p != q; p = p->next, q = q->next) ; return p;}两个升序链表的归并
Node* mergeOrderedList(Node* L1, Node* L2) { Node *p = L1->next, *q = L2->next, *tail = L1; L1->next = NULL; L2->next = NULL; delete L2; while (p != NULL && q != NULL) { Node* pp = p, *qq = q; if (pp->data < qq->data) { tail->next = pp; // 链表添加 pp 的节点 tail = tail->next; // 链表指针后移 p = p->next; // L1 的指针 p 后移 tail->next = NULL; } else { tail->next = qq; tail = tail->next; q = q->next; tail->next = NULL; } } // 此时应当至少有一条链表遍历结束了 if (p != NULL) tail->next = p; // 将剩余的元素拼接上去 else if (q != NULL) tail->next = q; return L1;}2.3.3. 双链表

struct Node { int data; Node * prior, * next;};1. 插入
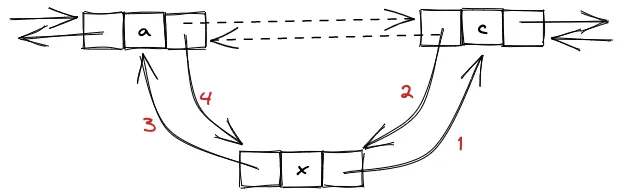
// 将 n 插入到 p 的后面n->data = n;n->next = p->next;p->next->prior = n;n->prior = p;p->next = n;2. 删除
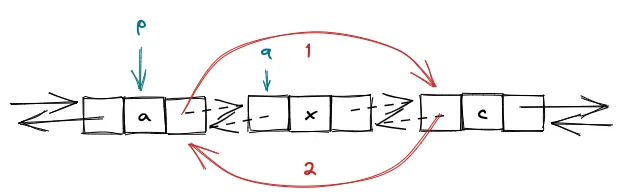
// 删除 p 的后继节点 qp->next = q->next;q->next->prior = p;delete(q);