第 4 章 串
4.2. 串的模式匹配
4.2.1. 简单的模式匹配算法
function strMatch(s1: string, s2: string): number { let i = 0 let j = 0 while (i < s1.length && j < s2.length) { if (s1[i] === s2[j]) { i++ j++ } else { i = i - j + 1 j = 0 } } if (j >= s2.length) return i - s2.length else return -1}4.2.2. KMP 算法
例如,想要从 ababcabcacbab 中匹配 abcac,用暴力法就会出现下面的情况
| 索引 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原串 | |||||||||||||
| 第 1 次 | |||||||||||||
| 第 2 次 | |||||||||||||
| 第 3 次 | |||||||||||||
| 第 4 次 | |||||||||||||
| 第 5 次 | |||||||||||||
| 第 6 次 |
可以发现,这种情况下,效率就相对比较差。我们希望在副串移动时直接移动到合适的位置,并且 不应该回溯。
| 索引 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原串 | |||||||||||||
| 第 1 次 | |||||||||||||
| 第 2 次 | |||||||||||||
| 第 3 次 |
右移位数 = 已匹配的字符数 - 对应部分的匹配值
Move = j - PM[j - 1]使用部分匹配值时,每当匹配失败,就去找他前一个元素的部分匹配值,这样有些别扭,那就不妨把 PM 表右移一位,这样哪个元素匹配失败,直接看他自己的部分匹配值即可。
| -1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
于是,上式改写成
Move = j - next[j]相当于回退到
j = j - Move = j - (j - next[j]) = next[j]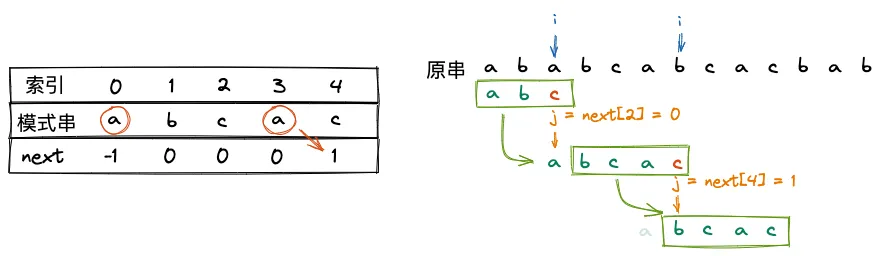
模式串与 next 数组
function getNext(t: string, next: number[]) { let i = 0 let j = -1 next[0] = -1 while (i < t.length - 1) { if (j === -1 || t[i] === t[j]) { ++i ++j next[i] = j } else { j = next[j] } }}
function kmp(s: string, t: string, next: number[]): number { let i = 0 let j = 0 while (i < s.length && j < t.length) { if (j === -1 || s[i] === t[j]) { ++i ++j } else { j = next[j] } } if (j >= t.length) return i - t.length else return -1}
const t = 'abcac'const next = Array(t.length).fill(0)
getNext(t, next)const i = kmp('ababcabcacbab', t, next)console.log(next, i)// [-1, 0, 0, 0, 1] 54.2.3. KMP 算法的优化
next 数组在某些情况下仍然有一些缺陷,还可以进一步优化,例如 aaaab 与 aaabaaaab 的匹配
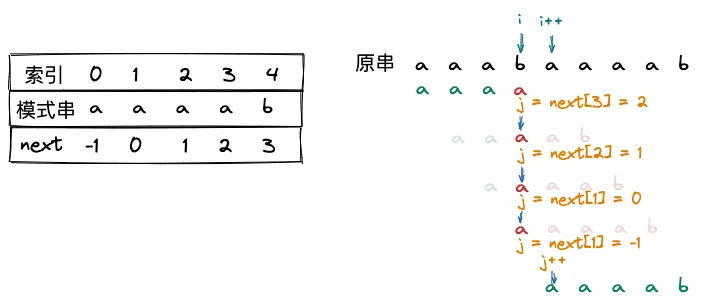
中间多了 3 次多余的匹配,因此我们可以考虑将它优化。
观察到,当 s[3] != p[3] 时,如果用 next 数组,还需要 s[3] 与 p[2], p[1], p[0] 分别匹配。
此时应当注意到,不应该出现 p[j] == p[next[j]],因为当 p[j] != s[j] 时,下一次比较必然是 p[next[j]] 和 s[j],因此需要 递归 一下,将 next[j] 修正为 next[next[j]],直至两者不相等为止。
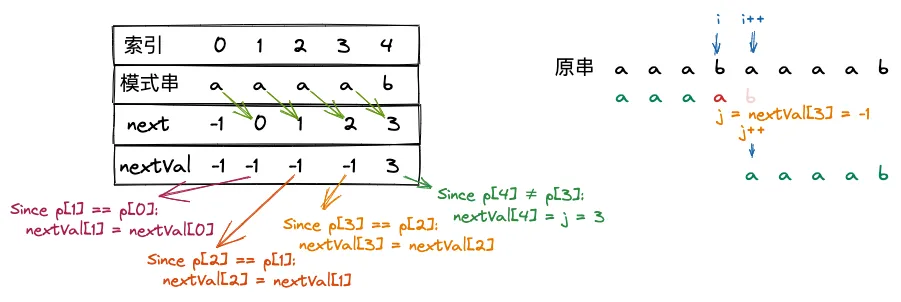
function getNextVal(t: string, nextVal: number[]) { let i = 0 let j = -1 nextVal[0] = -1 while (i < t.length - 1) { if (j === -1 || t[i] === t[j]) { ++i ++j if (t[i] !== t[j]) nextVal[i] = j else nextVal[i] = nextVal[j] } else { j = nextVal[j] } }}
function kmp(s: string, t: string, next: number[]): number { let i = 0 let j = -1 while (i < s.length && j < t.length) { if (j === -1 || s[i] === t[j]) { ++i ++j } else { j = next[j] } } if (j >= t.length) return i - t.length else return -1}
const t = 'aaaab'const next = Array(t.length).fill(0)
getNextVal(t, next)const i = kmp('aaabaaaab', t, next)console.log(next, i)// [-1, -1, -1, -1, 3] 4